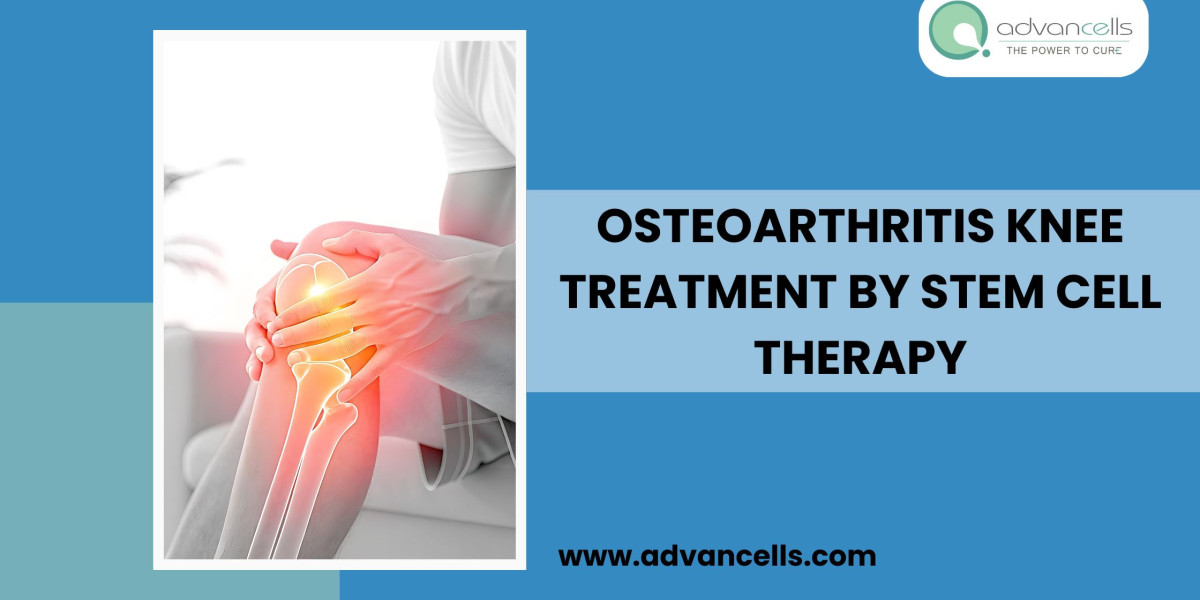
Arthritis is a disorder of joints, and osteoarthritis is its most prevalent form. It targets joint cartilage, which protects bones and enables their smooth gliding over each other. In osteoarthritis, the degeneration of cartilage causes the bones in the joints to rub against one another, which causes stiffness and discomfort. It is prominent in the hips and knees. Its multitude of causative factors has raised its global incidence, making it a significant health concern.
While many Osteoarthritis Knee Treatment are available, they cannot repair cartilage and only provide relief from the symptoms. The disorder eventually results in disability, declining the quality of life for several patients. The advent of regenerative medicine has introduced a new approach to conventional treatment modalities. It aims to repair and cause functional recovery instead of slowing disease progression. Stem cell therapy has shown fascinating potential in the field, sparking hope among many.
Osteoarthritis Causes
Breakdown of cartilage is the primary osteoarthritis cause. It can occur owing to various risk factors.
- Age: The aging process naturally deteriorates tissue, including joints, thereby increasing the chances of this disorder.
- Gender: Females are more prone to developing the disorder due to hormonal changes after menopause.
- Genetic Factors: Several genetic variants have been identified that predispose individuals towards osteoarthritis.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases the load on joints, especially in the knees and hips, augmenting the risk of the disorder.
- Injury: Any injury to joints can initiate damage to cartilage or accelerate it.
- Mechanical Stress: In addition to injury, movements during specific jobs or sports can put repetitive stress on joints, accelerating cartilage damage.
- Bone Disorders: Several disorders, such as osteoporosis, rickets, congenital joint disorder, Paget disease, etc., weaken bones, leading to the development of osteoporosis.
When osteoarthritis occurs due to a pre-existing joint abnormality, it is referred to as secondary osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis Symptoms
Osteoarthritis worsen over time, progressing from mild pain to joint disability. The common symptoms include:
- Joint pain: Initially mild, pain tends to increase with activity and lessen with rest.
- Stiffness: A sense of tightness in joints is noticeable, usually after periods of inactivity or early in the morning.
- Swelling: Inflammation and fluid accumulation may occur around the affected joint.
- Decreased range of motion: The joint loses flexibility as the disease progresses.
- Grinding or cracking sounds: Known as crepitus, these occur when bones rub together.
- Joint deformities: Advanced stages can cause changes in joint shape and alignment.
As the pain becomes more persistent, it interferes with regular joint movement and daily activities.